RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Chapter 20 Mensuration - I (Area of a Trapezium and a Polygon) Free Online
EXERCISE 20.1 PAGE NO: 20.13
1. A flooring tile has the shape of a parallelogram whose base is 24 cm and the corresponding height is 10 cm. How many such tiles are required to cover a floor of area 1080 m2?
Solution:
Given that,
Base of parallelogram = 24cm
Height of parallelogram = 10cm
Area of floor = 1080m2
We know that,
Area of parallelogram = Base × Height
Area of 1 tile = 24 × 10 = 240cm2
We know that, 1m = 100cm
So for 1080m2 = 1080 × 100 × 100 cm2
To calculate the Number of tiles required = Area of floor/Area of 1 tile
i.e., Number of tiles required = (1080 × 100 × 100) / (24 × 10) = 45000
∴ Number of tiles required = 45000
2. A plot is in the form of a rectangle ABCD having semi-circle on BC as shown in Fig. 20.23. If AB = 60 m and BC = 28 m, Find the area of the plot.
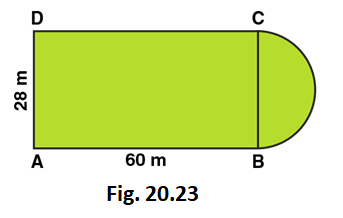
Solution:
Area of the plot = Area of the rectangle + Area of semi-circle
Radius of semi-circle = BC/2 = 28/2 = 14m
Area of the Rectangular plot = Length × Breadth = 60 × 28 = 1680 m2
Area of the Semi-circular portion = πr2/2
= 1/2 × 22/7 × 14 × 14
= 308 m2
∴ The total area of the plot = 1680 + 308 = 1988 m2
3. A playground has the shape of a rectangle, with two semi-circles on its smaller sides as diameters, added to its outside. If the sides of the rectangle are 36 m and 24.5 m, find the area of the playground. (Take π= 22/7.)
Solution:
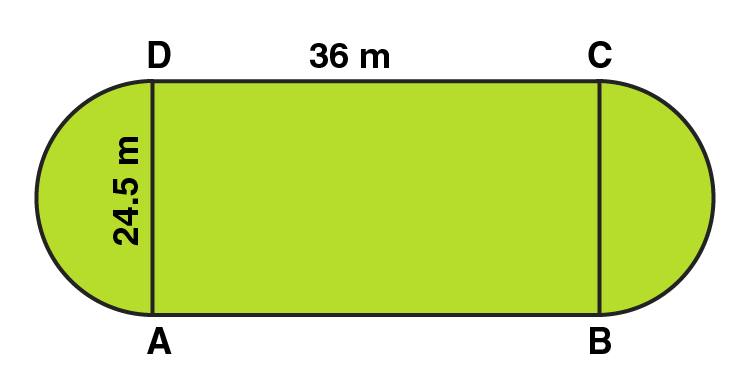
Area of the plot = Area of the Rectangle + 2 × area of one semi-circle
Radius of semi-circle = BC/2 = 24.5/2 = 12.25m
Area of the Rectangular plot = Length × Breadth = 36 × 24.5 = 882 m2
Area of the Semi-circular portions = 2 × πr2/2
= 2 × 1/2 × 22/7 × 12.25 × 12.25 = 471.625 m2
Area of the plot = 882 + 471.625 = 1353.625 m2
4. A rectangular piece is 20 m long and 15 m wide. From its four corners, quadrants of radii 3.5 m have been cut. Find the area of the remaining part.
Solution:
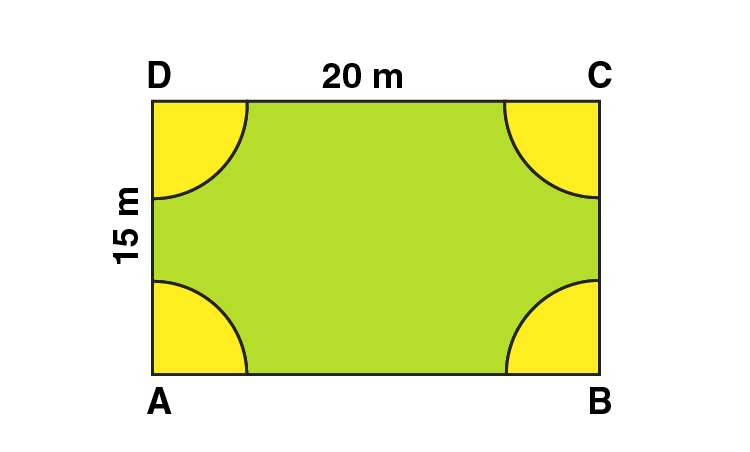
Area of the plot = Area of the rectangle – 4 × area of one quadrant
Radius of semi-circle = 3.5 m
Area of four quadrants = area of one circle
Area of the plot = Length × Breadth – πr2
Area of the plot = 20 × 15 – (22/7 × 3.5 × 3.5)
Area of the plot = 300 – 38.5 = 261.5 m2
5. The inside perimeter of a running track (shown in Fig. 20.24) is 400 m. The length of each of the straight portion is 90 m and the ends are semi-circles. If track is everywhere 14 m wide, find the area of the track. Also, find the length of the outer running track.
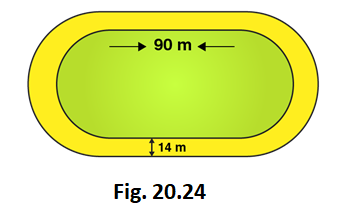
Solution:
Perimeter of the inner track = 2 × Length of rectangle + perimeter of two semi-circular ends
Perimeter of the inner track = Length + Length + 2πr
400 = 90 + 90 + (2 × 22/7 × r)
(2 × 22/7 × r) = 400 – 180
(2 × 22/7 × r) = 220
44r = 220 × 7
44r = 1540
r = 1540/44 = 35
r = 35m
So, the radius of inner circle = 35 m
Now, let’s calculate the radius of outer track
Radius of outer track = Radius of inner track + width of the track
Radius of outer track = 35 + 14 = 49m
Length of outer track = 2× Length of rectangle + perimeter of two outer semi-circular ends
Length of outer track = 2× 90 + 2πr
Length of outer track = 2× 90 + (2 × 22/7 × 49)
Length of outer track = 180 + 308 = 488
So, Length of outer track = 488m
Area of inner track = Area of inner rectangle + Area of two inner semi-circles
Area of inner track = Length × Breadth + πr2
Area of inner track = 90 × 70 + (22/7 × 35 × 35)
Area of inner track = 6300 + 3850
So, Area of inner track = 10150 m2
Area of outer track = Area of outer rectangle + Area of two outer semi-circles
Breadth of outer track = 35 + 35 +14 + 14 = 98 m
Area of outer track = length× breadth + πr2
Area of outer track = 90 × 98 + (22/7 × 49 × 49)
Area of outer track = 8820 + 7546
So, Area of outer track = 16366 m2
Now, let’s calculate area of path
Area of path = Area of outer track – Area of inner track
Area of path = 16366 – 10150 = 6216
So, Area of path = 6216 m2
6. Find the area of Fig. 20.25, in square cm, correct to one place of decimal. (Take π =22/7)
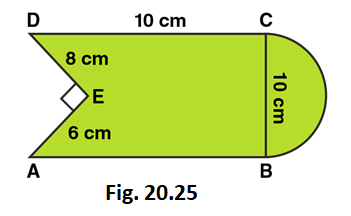

Solution:
Area of the Figure = Area of square + Area of semi-circle – Area of right angled triangle
Area of the Figure = side × side + πr2/2 – (1/2 × base × height)
Area of the Figure = 10 × 10 + (1/2 × 22/7 × 5 × 5) – (1/2 × 8 × 6)
Area of the Figure = 100 + 39.28 – 24
Area of the Figure = 115.3
So, Area of the Figure = 115.3 cm2
7. The diameter of a wheel of a bus is 90 cm which makes 315 revolutions per minute. Determine its speed in kilometres per hour. (Take π=22/7)
Solution:
Given that, Diameter of a wheel = 90 cm
We know that, Perimeter of wheel = 2πd
Perimeter of wheel = 22/7 × 90 = 282.857
So, Perimeter of a wheel = 282.857 cm
Distance covered in 315 revolutions = 282.857× 315 = 89099.955 cm
One km = 100000 cm
Therefore, Distance covered = 89099.955/100000 = 0.89 km
Speed in km per hour = 0.89 × 60 = 53.4 km per hour
8. The area of a rhombus is 240 cm2 and one of the diagonal is 16 cm. Find another diagonal.
Solution:
Area of rhombus = 1/2 × d1 × d2
240 = 1/2 × 16 × d2
240 = 8 × d2
d2 = 240/8 = 30
So, the other diagonal is 30 cm
9. The diagonals of a rhombus are 7.5 cm and 12 cm. Find its area.
Solution:
Area of rhombus = 1/2 × d1 × d2
Area of rhombus = 1/2 × 7.5 × 12
Area of rhombus = 6 × 7.5 = 45
So, Area of rhombus = 45 cm2
10. The diagonal of a quadrilateral shaped field is 24 m and the perpendiculars dropped on it from the remaining opposite vertices are 8 m and 13 m. Find the area of the field.
Solution:
Area of quadrilateral = 1/2 × d1 × (p1 + p2)
Area of quadrilateral = 1/2 × 24 × (8 + 13)
Area of quadrilateral = 12 × 21 = 252
So, Area of quadrilateral is 252 cm2
11. Find the area of a rhombus whose side is 6 cm and whose altitude is 4 cm. If one of its diagonals is 8 cm long, find the length of the other diagonal.
Solution:
Given that,
Side of rhombus = 6 cm
Altitude of rhombus = 4 cm
Since rhombus is a parallelogram, therefore area of parallelogram = base × altitude
i.e., Area of parallelogram = 6 × 4 = 24 cm2
Area of parallelogram = Area of rhombus
Area of rhombus = 1/2 × d1 × d2
24 = 1/2 × 8 × d2
24 = 4 × d2
d2 = 24/4 = 6
So, length of other diagonal of rhombus is 6 cm
12. The floor of a building consists of 3000 tiles which are rhombus shaped and each of its diagonals are 45 cm and 30 cm in length. Find the total cost of polishing the floor, if the cost per m2 is Rs. 4.
Solution:
We know that,
Area of rhombus = 1/2 × d1 × d2
Area of rhombus = 1/2 × 45 × 30
Area of rhombus = 1350/2 = 675
So, Area of rhombus = 675 cm2
∴ Area of one tile = 675 cm2
Now, Area of 3000 tiles = 675× 3000 = 2025000 cm2
Area of tiles in m2 = 2025000/10000 = 202.5 m2
Total cost for polishing the floor = 202.5× 4 = Rs 810
13. A rectangular grassy plot is 112 m long and 78 m broad. It has gravel path 2.5 m wide all around it on the side. Find the area of the path and the cost of constructing it at Rs. 4.50 per square metre.
Solution:
We know that,
Inner area of rectangle = length × breadth
Inner area of rectangle = 112 × 78 = 8736 m2
Width of path = 2.5 m
Length of outer rectangle = 112 – (2.5 + 2.5) = 107 m
Breadth of outer rectangle = 78 – (2.5 + 2.5) = 73 m
And,
Outer area of rectangle = length × breadth
Outer area of rectangle = 107 × 73 = 7811 m2
Now let’s calculate Area of path,
Area of path = Outer area of rectangle – Inner area of rectangle
Area of path = 8736 – 7811 = 925 m2
Also given that,
Cost of construction for 1 m2 = Rs 4.50
∴ Cost of construction for 925 m2 = 925 × 4.50 = Rs 4162.5
14. Find the area of a rhombus, each side of which measures 20 cm and one of whose diagonals is 24 cm.
Solution:
Given that,
Length of side of rhombus = 20 cm
Length of one diagonal = 24 cm
In ΔAOB,
Using Pythagoras theorem:
AB2 = OA2 + OB2
202 = 122 + OB2
OB2 = 202 – 122
OB2 = 400 – 144
OB2 = 256
OB = 16
So, length of the other diameter = 16 × 2 = 32 cm
Area of rhombus = 1/2 × d1 × d2
Area of rhombus = 1/2 × 24 × 32
Area of rhombus = 384 cm2
15. The length of a side of a square field is 4 m. What will be the altitude of the rhombus, if the area of the rhombus is equal to the square field and one of its diagonal is 2 m?
Solution:
Given that,
Length of a side of a square = 4 m
Area of square = side2
Area of square = 4 × 4 = 16 m2
We know that,
Area of square = Area of rhombus
So, Area of rhombus = 16 m2
Area of rhombus = 1/2 × d1 × d2
16 = 1/2 × 2 × d2
16 = d2
∴ the diagonal of rhombus = 16 m
In ΔAOB,
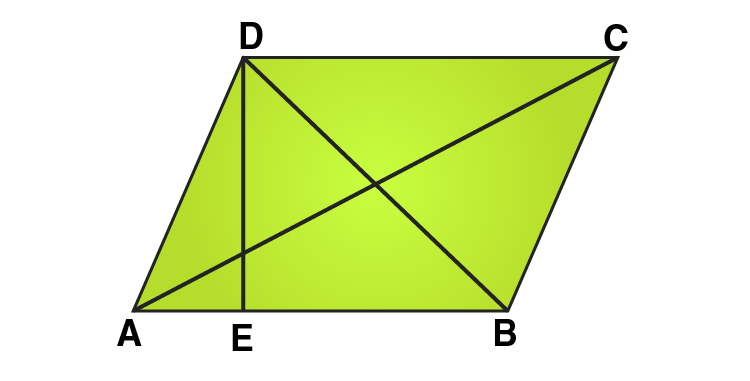
Using Pythagoras theorem:
AB2 = OA2 + OB2
AB2 = 82 + 12
AB2 = 65
AB = √65
Since rhombus is a parallelogram, therefore area of parallelogram = base × altitude
Area of parallelogram = AB × DE
16 = √65 × DE
DE = 16/√65
i.e., Altitude of Rhombus = 16/√65 cm
16. Find the area of the field in the form of a rhombus, if the length of each side be 14 cm and the altitude be 16 cm.
Solution:
Given that,
Side of rhombus = 14 cm
Altitude of rhombus = 16 cm
Since rhombus is a parallelogram, therefore
Area of parallelogram = base × altitude
Area of parallelogram = 14 × 16 = 224 cm2
17. The cost of fencing a square field at 60 paise per metre is Rs. 1200. Find the cost of reaping the field at the rate of 50 paise per 100 sq. metres.
Solution:
Perimeter of square field = Cost of fencing / rate of fencing
Perimeter of square field = 1200/0.6 = 2000
So, Perimeter of square field = 2000 m
Perimeter of square = 4 × side
Side of square = Perimeter / 4 = 2000/4 = 500
So, Side of square = 500 m
We know that, Area of square = side2
Area of square = 500 × 500 = 250000 m2
Cost of reaping = (250000 × 0.5) / 100 = 1250
∴ Cost of reaping the field is Rs 1250
18. In exchange of a square plot one of whose sides is 84 m, a man wants to buy a rectangular plot 144 m long and of the same area as of the square plot. Find the width of the rectangular plot.
Solution:
Area of square = side2
Area of square = 84 × 84 = 7056
Since, Area of square = Area of rectangle
7056 = 144 × width
Width = 7056/144 = 49
∴ Width of rectangle = 49 m
19. The area of a rhombus is 84 m2. If its perimeter is 40 m, then find its altitude.
Solution:
Given that,
Area of rhombus = 84 m2
Perimeter = 40 m
We know that,
Perimeter of rhombus = 4 × side
∴ Side of rhombus = Perimeter / 4 = 40/4 = 10
So, Side of rhombus = 10 m
Since rhombus is a parallelogram, therefore Area of parallelogram = base × altitude
84 = 10 × altitude
Altitude = 84/10 = 8.4
So, Altitude of rhombus = 8.4 m
20. A garden is in the form of a rhombus whose side is 30 metres and the corresponding altitude is 16 m. Find the cost of levelling the garden at the rate of Rs. 2 per m2.
Solution:
Given that,
Side of rhombus = 30 m
Altitude of rhombus = 16 m
Since rhombus is a parallelogram, therefore Area of parallelogram = base × altitude
Area of parallelogram = 30 × 16 = 480 m2
Cost of levelling the garden = area × rate
Cost of levelling the garden = 480 × 2 = 960
So, Cost of levelling the garden is Rs 960
21. A field in the form of a rhombus has each side of length 64 m and altitude 16 m. What is the side of a square field which has the same area as that of a rhombus?
Solution:
Given that,
Side of rhombus = 64 m
Altitude of rhombus = 16 m
Since rhombus is a parallelogram, therefore Area of parallelogram = base × altitude
Area of parallelogram = 64 × 16 = 1024 m2
Since Area of rhombus = Area of square
Therefore, Area of square = side2
Or side2 = Area of square
Side of a square = √square
Side of square = √1024 = 32
∴ Side of square = 32 m
22. The area of a rhombus is equal to the area of a triangle whose base and the corresponding altitude are 24.8 cm and 16.5 cm respectively. If one of the diagonals of the rhombus is 22 cm, find the length of the other diagonal.
Solution:
Given that,
Length of base of triangle = 24.8 cm
Length of altitude of triangle= 16.5 cm
∴ Area of triangle = 1/2 × base × altitude
Area of triangle = 1/2 × 24.8 × 16.5 = 204.6
So, Area of triangle = 204.6 cm
Since, Area of triangle = Area of rhombus
∴ Area of rhombus = 1/2 × d1 × d2
204.6 = 1/2 × 22 × d2
204.6 = 11 × d2
d2 = 204.6/11 = 18.6
∴ The length of other diagonal is 18.6 cm
EXERCISE 20.2 PAGE NO: 20.22
1. Find the area, in square metres, of the trapezium whose bases and altitudes are as under:
(i) bases = 12 dm and 20 dm, altitude = 10 dm
(ii) bases = 28 cm and 3 dm, altitude = 25 cm
(iii) bases = 8 m and 60 dm, altitude = 40 dm
(iv) bases = 150 cm and 30 dm, altitude = 9 dm
(i) bases = 12 dm and 20 dm, altitude = 10 dm
(ii) bases = 28 cm and 3 dm, altitude = 25 cm
(iii) bases = 8 m and 60 dm, altitude = 40 dm
(iv) bases = 150 cm and 30 dm, altitude = 9 dm
Solution:
(i) Given that,
Length of bases of trapezium = 12 dm and 20 dm
Length of altitude = 10 dm
We know that, 10 dm = 1 m
∴ Length of bases in m = 1.2 m and 2 m
Similarly, length of altitude in m = 1 m
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (1.2 + 2.0) × 1
Area of trapezium = 1/2 × 3.2 = 1.6
So, Area of trapezium = 1.6m2
(ii) Given that,
Length of bases of trapezium = 28 cm and 3 dm
Length of altitude = 25 cm
We know that, 10 dm = 1 m
∴ Length of bases in m = 0.28 m and 0.3 m
Similarly, length of altitude in m = 0.25 m
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (0.28 + 0.3) × 0.25
Area of trapezium = 1/2 × 0.58× 0.25 = 0.0725
So, Area of trapezium = 0.0725m2
(iii) Given that,
Length of bases of trapezium = 8 m and 60 dm
Length of altitude = 40 dm
We know that, 10 dm = 1 m
∴ Length of bases in m = 8 m and 6 m
Similarly, length of altitude in m = 4 m
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (8 + 6) × 4
Area of trapezium = 1/2 × 56 = 28
So, Area of trapezium = 28m2
(iv) Given that,
Length of bases of trapezium = 150 cm and 30 dm
Length of altitude = 9 dm
We know that, 10 dm = 1 m
∴ Length of bases in m = 1.5 m and 3 m
Similarly, length of altitude in m = 0.9 m
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (1.5 + 3) × 0.9
Area of trapezium = 1/2 × 4.5 × 0.9 = 2.025
So, Area of trapezium = 2.025m2
2. Find the area of trapezium with base 15 cm and height 8 cm, if the side parallel to the given base is 9 cm long.
Solution:
Given that,
Length of bases of trapezium = 15 cm and 9 cm
Length of altitude = 8 cm
We know that,
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (15 + 9) × 8
Area of trapezium = 1/2 × 192 = 96
So, Area of trapezium = 96m2
3. Find the area of a trapezium whose parallel sides are of length 16 dm and 22 dm and whose height is 12 dm.
Solution:
Given that,
Length of bases of trapezium = 16 dm and 22 dm
Length of altitude = 12 dm
We know that, 10 dm = 1 m
∴ Length of bases in m = 1.6 m and 2.2 m
Similarly, length of altitude in m = 1.2 m
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (1.6 + 2.2) × 1.2
Area of trapezium = 1/2 × 3.8 × 1.2 = 2.28
So, Area of trapezium = 2.28m2
4. Find the height of a trapezium, the sum of the lengths of whose bases (parallel sides) is 60 cm and whose area is 600 cm2.
Solution:
Given that,
Length of bases of trapezium = 60 cm
Area = 600 cm2
We know that,
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
600 = 1/2 (60) × altitude
600 = 30 × altitude
Which implies, altitude = 600/30 = 20
∴ Length of altitude is 20 cm
5. Find the altitude of a trapezium whose area is 65 cm2 and whose base are 13 cm and 26 cm.
Solution:
Given that,
Length of bases of trapezium = 13 cm and 26 cm
Area = 65 cm2
We know that,
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
65 = 1/2 (13 + 26) × altitude
65 = 39/2 × altitude
Which implies, altitude = (65×2) /39 = 130/39 = 10/3
∴ Length of altitude = 10/3 cm
6. Find the sum of the lengths of the bases of a trapezium whose area is 4.2 m2 and whose height is 280 cm.
Solution:
Given that,
Height of trapezium = 280 cm = 2.8m
Area = 4.2 m2
We know that,
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude To calculate the length of parallel sides we can rewrite the above equation as,
Sum of lengths of parallel sides = (2 × Area) / altitude
Sum of lengths of parallel sides = (2 × 4.2) / 2.8 = 8.4/2.8 = 3
∴ Sum of lengths of parallel sides = 3 m
7. Find the area of a trapezium whose parallel sides of lengths 10 cm and 15 cm are at a distance of 6 cm from each other. Calculate this area as,
(i) the sum of the areas of two triangles and one rectangle.
(ii) the difference of the area of a rectangle and the sum of the areas of two triangles.
(i) the sum of the areas of two triangles and one rectangle.
(ii) the difference of the area of a rectangle and the sum of the areas of two triangles.
Solution:
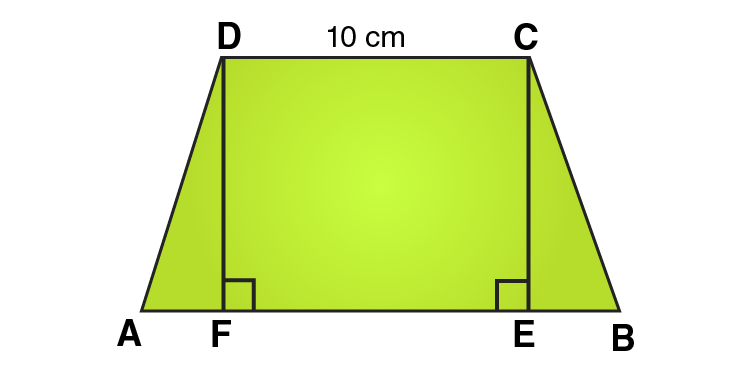
We know that, Area of a trapezium ABCD
= area (∆DFA) + area (rectangle DFEC) + area (∆CEB)
= (1/2 × AF × DF) + (FE × DF) + (1/2 × EB × CE)
= (1/2 × AF × h) + (FE × h) + (1/2 × EB × h)
= 1/2 × h × (AF + 2FE + EB)
= 1/2 × h × (AF + FE + EB + FE)
= 1/2 × h × (AB + FE)
= 1/2 × h × (AB + CD) [Opposite sides of rectangle are equal]
= 1/2 × 6 × (15 + 10)
= 1/2 × 6 × 25 = 75
∴ Area of trapezium = 75 cm2
8. The area of a trapezium is 960 cm2. If the parallel sides are 34 cm and 46 cm, find the distance between them.
Solution:
We know that,
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × distance between parallel sides
i.e., Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of sides) × distance between parallel sides
To calculate the distance between parallel sides we can rewrite the above equation as,
Distance between parallel sides = (2 × Area) / Sum of sides
= (2 × 960) / (34 + 46)
= (2 × 960) / 80 = 1920/80 = 24
∴ Distance between parallel sides = 24 cm
9. Find the area of Fig. 20.35 as the sum of the areas of two trapezium and a rectangle.
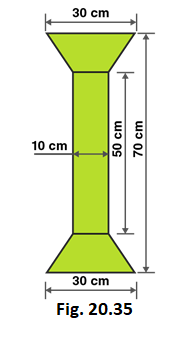

Solution:
From the figure we can write,
Area of figure = Area of two trapeziums + Area of rectangle
Given that,
Length of rectangle = 50 cm
Breadth of rectangle = 10 cm
Length of parallel sides of trapezium = 30 cm and 10 cm
Distance between parallel sides of trapezium = (70–50)/2 = 20/2 = 10
So, Distance between parallel sides of trapezium = 10 cm
Area of figure = 2 × 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude + Length × Breadth
Area of figure = 2 × 1/2 (30+10) × 10 + 50 × 10
Area of figure = 40 × 10 + 50 × 10
Area of figure = 400 + 500 = 900
∴ Area of figure = 900 cm2
10. Top surface of a table is trapezium in shape. Find its area if its parallel sides are 1 m and 1.2 m and perpendicular distance between them is 0.8 m.
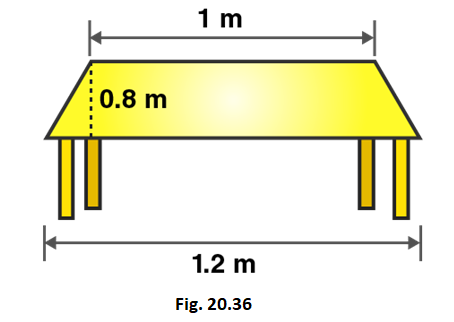

Solution:
Given that,
Length of parallel sides of trapezium = 1.2m and 1m
Distance between parallel sides of trapezium = 0.8m
We know that,
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × distance between parallel sides
i.e., Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of sides) × distance between parallel sides
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (1.2 + 1) × 0.8
Area of trapezium = 1/2 × 2.2 × 0.8 = 0.88
So, Area of trapezium = 0.88m2
11. The cross-section of a canal is a trapezium in shape. If the canal is 10 m wide at the top 6 m wide at the bottom and the area of cross-section is 72 m2 determine its depth.
Solution:
Given that,
Length of parallel sides of trapezium = 10m and 6m
Area = 72 m2
Let the distance between parallel sides of trapezium = x meter
We know that,
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × distance between parallel sides
i.e., Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of sides) × distance between parallel sides
72 = 1/2 (10 + 6) × x
72 = 8 × x
x = 72/8 = 9
∴ The depth is 9m.
12. The area of a trapezium is 91 cm2 and its height is 7 cm. If one of the parallel sides is longer than the other by 8 cm, find the two parallel sides.
Solution:
Given that,
Let the length of one parallel side of trapezium = x meter
Length of other parallel side of trapezium = (x+8) meter
Area of trapezium = 91 cm2
Height = 7 cm
We know that,
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
91 = 1/2 (x+x+8) × 7
91 = 1/2(2x+8) × 7
91 = (x+4) × 7
(x+4) = 91/7
x+4 = 13
x = 13 – 4
x = 9
∴ Length of one parallel side of trapezium = 9 cm
And, Length of other parallel side of trapezium = x+8 = 9+8 = 17 cm
13. The area of a trapezium is 384 cm2. Its parallel sides are in the ratio 3:5 and the perpendicular distance between them is 12 cm. Find the length of each one of the parallel sides.
Solution:
Given that,
Let the length of one parallel side of trapezium = 3x meter
Length of other parallel side of trapezium = 5x meter
Area of trapezium = 384 cm2
Distance between parallel sides = 12 cm
We know that,
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × distance between parallel sides
i.e., Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of sides) × distance between parallel sides
384 = 1/2 (3x + 5x) × 12
384 = 1/2 (8x) × 12
4x = 384/12
4x = 32
x = 8
∴ Length of one parallel side of trapezium = 3x = 3× 8 = 24 cm
And, Length of other parallel side of trapezium = 5x = 5× 8 = 40 cm
14. Mohan wants to buy a trapezium shaped field. Its side along the river is parallel and twice the side along the road. If the area of this field is 10500 m2 and the perpendicular distance between the two parallel sides is 100 m, find the length of the side along the river.
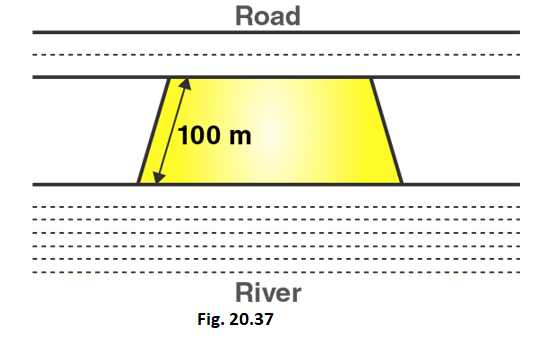

Solution:
Given that,
Let the length of side of trapezium shaped field along road = x meter
Length of other side of trapezium shaped field along road = 2x meter
Area of trapezium = 10500 cm2
Distance between parallel sides = 100 m
We know that,
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × distance between parallel sides
i.e., Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of sides) × distance between parallel sides
10500 = 1/2 (x + 2x) × 100
10500 = 1/2 (3x) × 100
3x = 10500/50
3x = 210
x = 210/3 = 70
x = 70
∴ Length of side of trapezium shaped field along road = 70 m
And, Length of other side of trapezium shaped field along road = 2x = 70× 2 = 140 m
15. The area of a trapezium is 1586 cm2 and the distance between the parallel sides is 26 cm. If one of the parallel sides is 38 cm, find the other.
Solution:
Given that,
Let the length of other parallel side of trapezium = x cm
Length of one parallel side of trapezium = 38 cm
Area of trapezium = 1586 cm2
Distance between parallel sides = 26 cm
We know that,
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × distance between parallel sides
i.e., Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of sides) × distance between parallel sides
1586 = 1/2 (x + 38) × 26
1586 = (x + 38) × 13
(x + 38) = 1586/13
x = 122 – 38
x =84
∴ Length of the other parallel side of trapezium = 84 cm
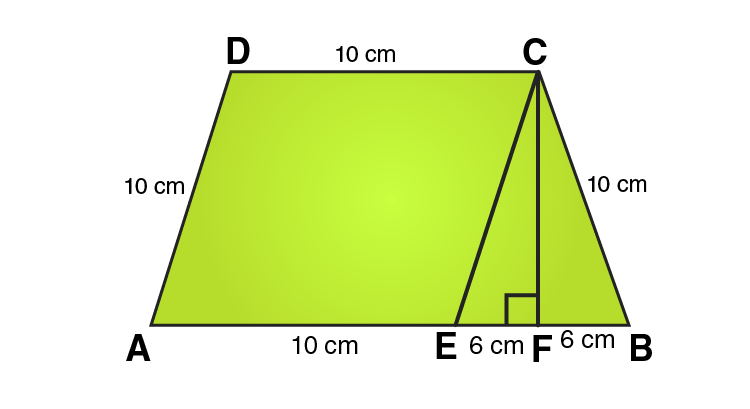
16. The parallel sides of a trapezium are 25 cm and 13 cm; its nonparallel sides are equal, each being 10 cm, find the area of the trapezium.
Solution:
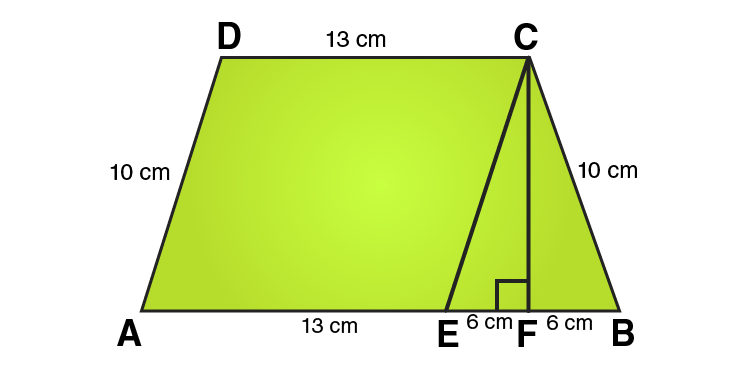
In ΔCEF,
CE = 10 cm and EF = 6cm
Using Pythagoras theorem:
CE2 = CF2 + EF2
CF2 = CE2 – EF2
CF2 = 102 – 62
CF2 = 100-36
CF2 = 64
CF = 8 cm
From the figure we can write,
Area of trapezium = Area of parallelogram AECD + Area of area of triangle CEF
Area of trapezium = base × height + 1/2 (base × height)
Area of trapezium = 13 × 8 + 1/2 (12 × 8)
Area of trapezium = 104 + 48 = 152
∴ Area of trapezium = 152 cm2
17. Find the area of a trapezium whose parallel sides are 25 cm, 13 cm and the other sides are 15 cm each.
Solution:
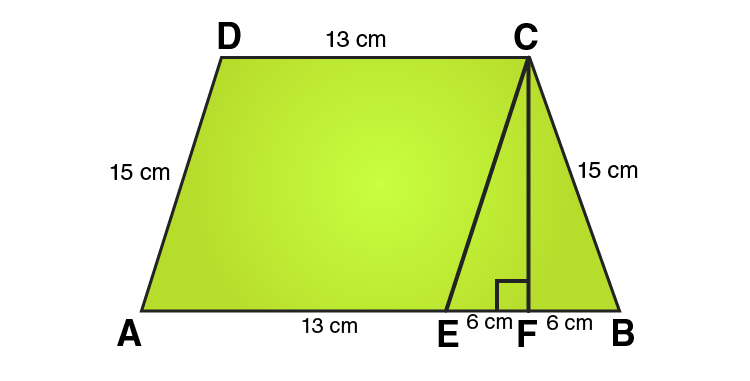
In ΔCEF,
CE = 10 cm and EF = 6cm
Using Pythagoras theorem:
CE2 = CF2 + EF2
CF2 = CE2 – EF2
CF2 = 152 – 62
CF2 = 225-36
CF2 = 189
CF = √189
= √ (9×21)
= 3√21 cm
From the figure we can write,
Area of trapezium = Area of parallelogram AECD + Area of area of triangle CEF
Area of trapezium = height + 1/2 (sum of parallel sides)
Area of trapezium = 3√21 × 1/2 (25 + 13)
Area of trapezium = 3√21 × 19 = 57√21
∴ Area of trapezium = 57√21 cm2
18. If the area of a trapezium is 28 cm2 and one of its parallel sides is 6 cm, find the other parallel side if its altitude is 4 cm.
Solution:
Given that,
Let the length of other parallel side of trapezium = x cm
Length of one parallel side of trapezium = 6 cm
Area of trapezium = 28 cm2
Length of altitude of trapezium = 4 cm
We know that,
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × distance between parallel sides
i.e., Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of sides) × distance between parallel sides
28 = 1/2 (6 + x) × 4
28 = (6 + x) × 2
(6 + x) = 28/2
(6 + x) = 14
x = 14 – 6
x = 8
∴ Length of the other parallel side of trapezium = 8 cm
19. In Fig. 20.38, a parallelogram is drawn in a trapezium, the area of the parallelogram is 80 cm2, find the area of the trapezium.
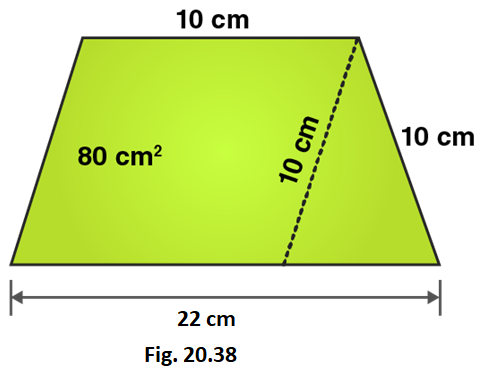

Solution:
In ΔCEF,
CE = 10 cm and EF = 6cm
Using Pythagoras theorem:
CE2 = CF2 + EF2
CF2 = CE2 – EF2
CF2 = 102 – 62
CF2 = 100-36
CF2 = 64
CF = 8 cm
Area of parallelogram = 80 cm2
From the figure we can write,
Area of trapezium = Area of parallelogram AECD + Area of area of triangle CEF
Area of trapezium = base × height + 1/2 (base × height)
Area of trapezium = 10 × 8 + 1/2 (12 × 8)
Area of trapezium = 80 + 48 = 128
∴ Area of trapezium = 128 cm2
20. Find the area of the field shown in Fig. 20.39 by dividing it into a square, a rectangle and a trapezium.
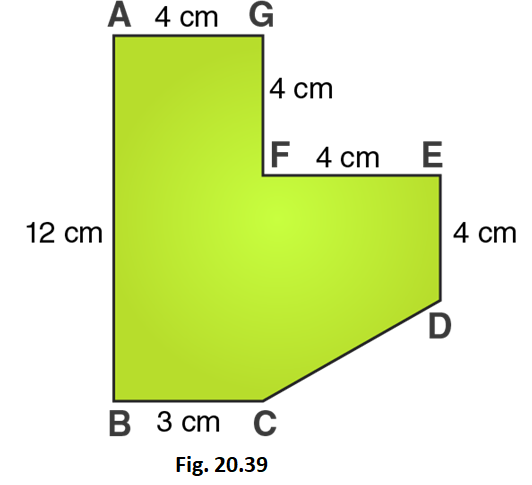

Solution:
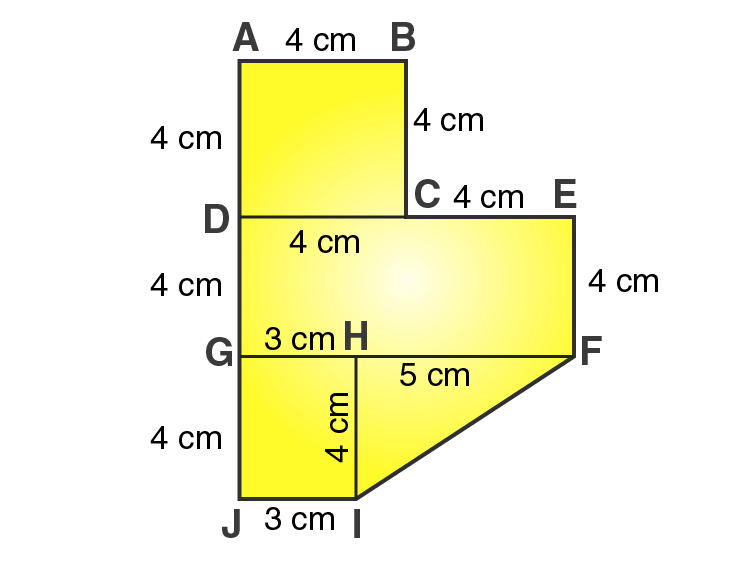
From the figure we can write,
Area of given figure = Area of square ABCD + Area of rectangle DEFG + Area of rectangle GHIJ + Area of triangle FHI
i.e., Area of given figure = side × side + length × breadth + length × breadth + 1/2 × base × altitude
Area of given figure = 4×4 + 8×4 + 3×4 + 1/2×5×5
Area of given figure = 16 + 32 + 12 + 10 = 70
∴ Area of given figure = 70 cm2
EXERCISE 20.3 PAGE NO: 20.28
1. Find the area of the pentagon shown in fig. 20.48, if AD = 10 cm, AG = 8 cm, AH = 6 cm, AF = 5 cm, BF = 5 cm, CG = 7 cm and EH = 3 cm.
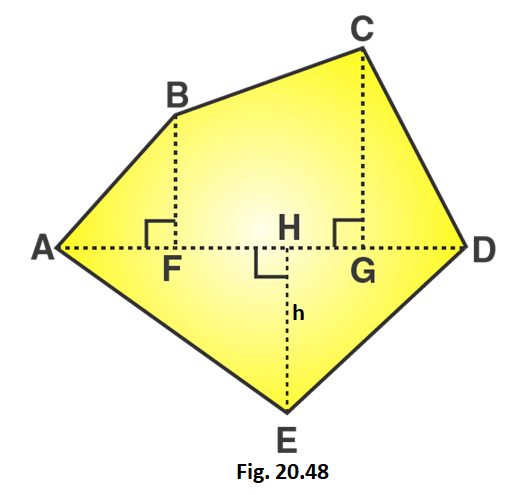

Solution:
GH = AG – AH = 8 – 6 = 2 cm
HF = AH – AF = 6 – 5 = 1 cm
GD = AD – AG = 10 – 8 = 2 cm
From the figure we can write,
Area of given figure = Area of triangle AFB + Area of trapezium BCGF + Area of triangle CGD + Area of triangle AHE + Area of triangle EGD
We know that,
Area of right angled triangle = 1/2 × base × altitude
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
Area of given pentagon = 1/2 × AF × BF + 1/2 (CG + BF) × FG + 1/2 × GD × CG + 1/2 × AH × EH + 1/2 × HD × EH
Area of given pentagon = 1/2 × 5 × 5 + 1/2 (7 + 5) × 3 + 1/2 × 2 × 7 + 1/2 × 6 × 3 + 1/2 × 4 × 3
Area of given pentagon = 12.5 + 18 + 7 + 9 + 6 = 52.5
∴ Area of given pentagon = 52.5 cm2
2. Find the area enclosed by each of the following figures [fig. 20.49 (i)-(ii)] as the sum of the areas of a rectangle and a trapezium.
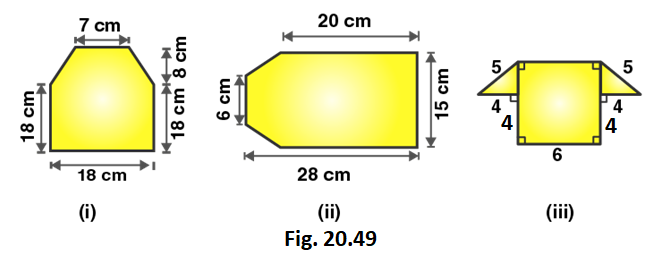

Solution:
Figure (i)
From the figure we can write,
Area of figure = Area of trapezium + Area of rectangle
Area of figure = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude + Length × Breadth
Area of figure = 1/2 (18 + 7) × 8 + 18 × 18
Area of figure = 1/2 (25) × 8 + 18 × 18
Area of figure =
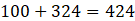
∴ Area of figure is 424 cm2
Figure (ii)
From the figure we can write,
Area of figure = Area of trapezium + Area of rectangle
Area of figure = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude + Length × Breadth
Area of given figure = 1/2 (15 + 6) × 8 + 15 × 20
Area of given figure = 84 + 300 = 384
∴ Area of figure is 384 cm2
Figure (iii)
Using Pythagoras theorem in the right angled triangle,
52 = 42 + x2
x2 = 25 – 16
x2 = 9
x = 3 cm
From the figure we can write,
Area of figure = Area of trapezium + Area of rectangle
Area of figure = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude + Length × Breadth
Area of given figure = 1/2 (14 + 6) × 3 + 4 × 6
Area of given figure = 30 + 24 = 54
∴ Area of figure is 54 cm2
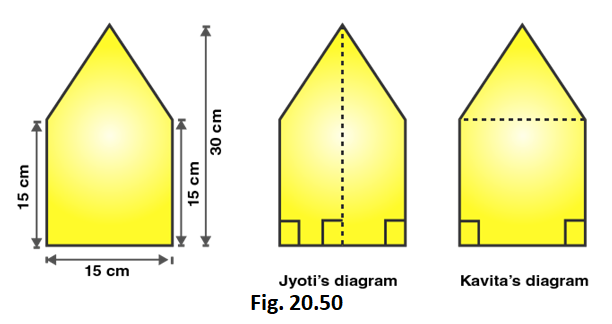
3. There is a pentagonal shaped park as shown in Fig. 20.50. Jyoti and Kavita divided it in two different ways.
Find the area of this park using both ways. Can you suggest some another way of finding its area?
Find the area of this park using both ways. Can you suggest some another way of finding its area?
Solution:
From the figure we can write,
Area of figure = Area of trapezium + Area of rectangle
Area of Jyoti’s diagram = 2 × 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
Area of figure = 2 × 1/2 × (15 + 30) × 7.5
Area of figure = 45 × 7.5 = 337.5
Therefore, Area of figure = 337.5 cm2
We also know that,
Area of Pentagon = Area of triangle + area of rectangle
Area of Pentagon = 1/2 × Base × Altitude + Length × Breadth
Area of Pentagon = 1/2 × 15 × 15 + 15 × 15
Area of Pentagon = 112.5 + 225 = 337.5
∴ Area of pentagon is 337.5 m2
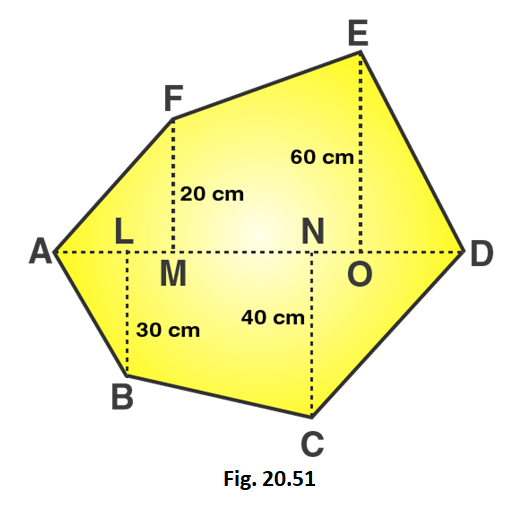
4. Find the area of the following polygon, if AL = 10 cm, AM = 20 cm, AN = 50 cm. AO = 60 cm and AD = 90 cm.
Solution:
Given that,
AL = 10 cm; AM = 20 cm; AN = 50 cm; AO = 60 cm; AD = 90 cm
LM = AM – AL = 20 – 10 = 10 cm
MN = AN – AM = 50 – 20 = 30 cm
OD = AD – AO = 90 – 60 = 30 cm
ON = AO – AN = 60 – 50 = 10 cm
DN = OD + ON = 30 + 10 = 40 cm
OM = MN + ON = 30 + 10 = 40 cm
LN = LM + MN = 10 + 30 = 40 cm
From the figure we can write,
Area of figure = Area of triangle AMF + Area of trapezium FMNE + Area of triangle END + Area of triangle ALB + Area of trapezium LBCN + Area of triangle DNC
We know that,
Area of right angled triangle = 1/2 × base × altitude
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
Area of given hexagon = 1/2 × AM × FM + 1/2 (MF + OE) × OM + 1/2 × OD × OE + 1/2 × AL × BL + 1/2 × (BL + CN) × LN + 1/2 × DN × CN
Area of given hexagon = 1/2 × 20 × 20 + 1/2 (20 + 60) × 40 + 1/2 × 30 × 60 + 1/2 × 10 × 30 + 1/2 × (30 + 40) × 40 + 1/2 × 40 × 40
Area of given hexagon = 200 + 1600 + 900 + 150 + 1400 + 800 = 5050
∴ Area of given hexagon is 5050 cm2
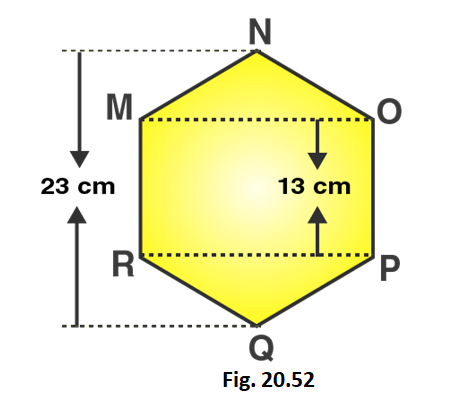
5. Find the area of the following regular hexagon.

Solution:
Given that,
NQ = 23 cm
ND + QC = 23 -13 = 10
ND = QC = 5 cm
OM = 24 cm
Area of given hexagon = 2 times Area of triangle MNO + Area of rectangle MOPR
Area of right angled triangle = 1/2 × base × altitude
Area of rectangle = length × breadth
Area of regular hexagon = 1/2 × OM × ND + MO × OP + 1/2 × RP × QC
Area of regular hexagon = 1/2 × 24 × 5 + 24 × 13 + 1/2 × 24 × 5
Area of given hexagon = 1/2 × 120 + 312 + 1/2 × 120 = 432
∴ Area of given hexagon is 432 cm2
